-
MDACT Physics
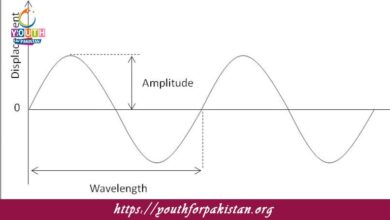
Progressive Waves MDCAT Quiz with Answers
Progressive waves are waves that transfer energy through a medium with no permanent displacement of the medium itself. In such waves, the disturbance moves from…
Read More » -
MDACT Physics
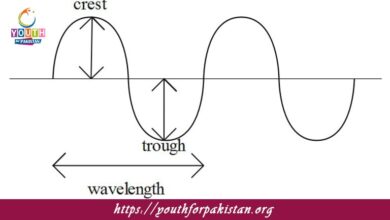
Crest MDCAT Quiz with Answers
The crest of a wave refers to the point of maximum displacement above the equilibrium position in a transverse wave. Otherwise, it’s the highest point…
Read More » -
MDACT Physics
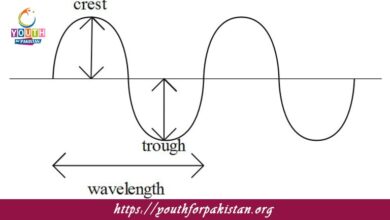
Trough MDCAT Quiz with Answers
The trough is the maximum displacement below the equilibrium position of a wave in a transverse wave. This is the point that represents the lowest…
Read More » -
MDACT Physics
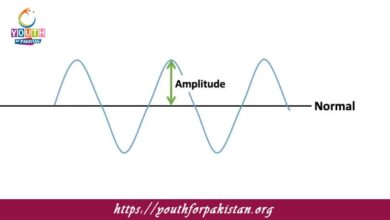
Amplitude MDCAT Quiz with Answers
The amplitude of a wave is defined as the maximum displacement of the wave from its equilibrium position. For a transverse wave, it is the…
Read More » -
MDACT Physics
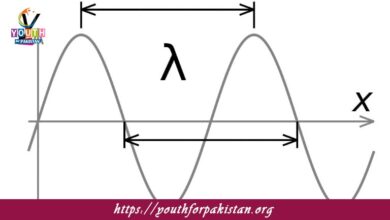
Wavelength MDCAT Quiz with Answers
Wavelength refers to the distance between two successive points in phase on a wave, such as from one crest to the next crest or from…
Read More » -
MDACT Physics
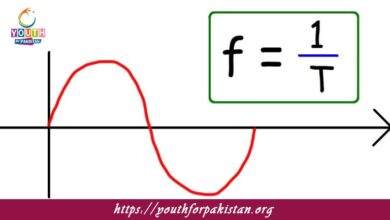
Time Period And Frequency MDCAT Quiz with Answers
Time period and frequency are two fundamental properties of periodic waves that are inversely related. These properties tell how frequently a wave wobbles in a…
Read More » -
MDACT Physics
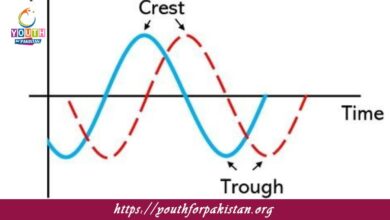
Types Of Progressive Waves MDCAT Quiz with Answers
Progressive waves are those waves that transfer energy from one place to another without any material displacement of the medium itself. Two main types can…
Read More » -
MDACT Physics
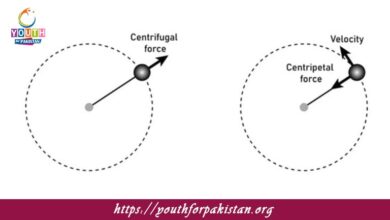
Centripetal Force MDCAT Quiz with Answers
Centripetal force is the force that keeps an object moving in a circular path, directed towards the center of the circle. In essence, it is…
Read More » -
MDACT Physics
Rotational And Circular Motion MDCAT Quiz with Answers
Rotational and circular motion refer to the motion of an object in a circular path or around an axis. These are very important concepts in…
Read More » -
MDACT Physics
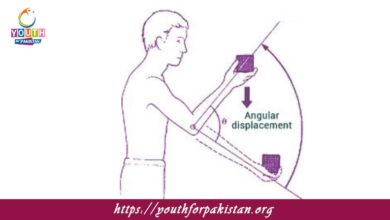
Angular Displacement MDCAT Quiz with Answers
Angular displacement is the angle by which an object rotates in a given time period. It is a vector quantity; hence, it has a magnitude…
Read More »
