Enzymes MDCAT MCQs with Answers
Welcome to the Enzymes MDCAT MCQs with Answers. In this post, we have shared Enzymes Multiple Choice Questions and Answers for PMC MDCAT 2024. Each question in MDCAT Chemistry offers a chance to enhance your knowledge regarding Enzymes MCQs in this MDCAT Online Test.
Enzymes are primarily composed of:
a) Carbohydrates
b) Lipids
c) Proteins
d) Nucleic acids
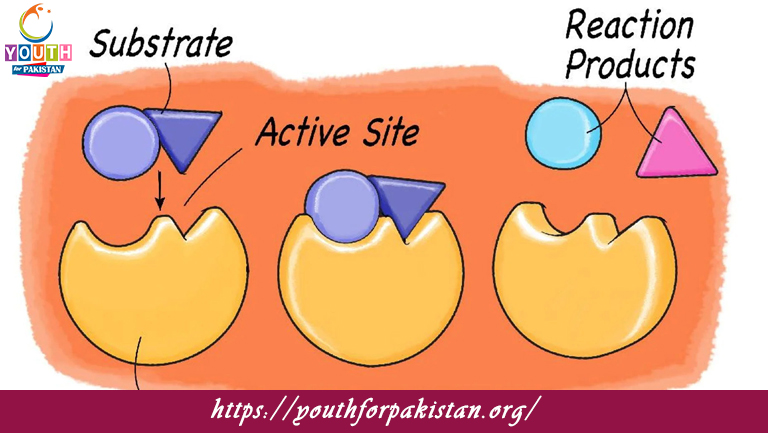
The part of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind is called the:
a) Active site
b) Allosteric site
c) Binding pocket
d) Regulatory site
Enzymes that catalyze the transfer of functional groups are known as:
a) Oxidoreductases
b) Transferases
c) Hydrolases
d) Ligases
Which of the following is a coenzyme that is involved in redox reactions?
a) Vitamin C
b) Vitamin D
c) Vitamin B12
d) Vitamin K
Enzymes that catalyze the breaking of peptide bonds are known as:
a) Lipases
b) Proteases
c) Amylases
d) Polymerases
The model describing enzyme action that suggests the enzyme changes its shape to accommodate the substrate is:
a) Lock and key model
b) Induced fit model
c) Enzyme-substrate complex model
d) Competitive inhibition model
Enzymes that catalyze the addition of a phosphate group to a molecule are called:
a) Phosphatases
b) Kinases
c) Ligases
d) Hydrolases
Which of the following factors does NOT affect enzyme activity?
a) Temperature
b) pH
c) Substrate concentration
d) Pressure
The rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction can be increased by:
a) Decreasing substrate concentration
b) Increasing enzyme concentration
c) Increasing temperature beyond the optimum
d) Increasing pH beyond the optimum
Inhibition where the inhibitor binds to the enzyme at a different site than the active site is known as:
a) Competitive inhibition
b) Non-competitive inhibition
c) Uncompetitive inhibition
d) Irreversible inhibition
The efficiency of an enzyme can be measured by its:
a) Km value
b) Vmax value
c) Turnover number
d) Binding affinity
The enzyme-substrate complex forms at the:
a) Active site
b) Allosteric site
c) Regulatory site
d) Binding site
Enzymes that are involved in DNA replication and repair are known as:
a) Polymerases
b) Ligases
c) Nucleases
d) Isomerases
The concept that an enzyme undergoes a change in shape upon substrate binding is called:
a) Lock and key hypothesis
b) Induced fit hypothesis
c) Enzyme-substrate specificity
d) Enzyme catalysis
Which type of enzyme inhibition cannot be overcome by increasing substrate concentration?
a) Competitive inhibition
b) Non-competitive inhibition
c) Uncompetitive inhibition
d) Allosteric inhibition
Enzymes that catalyze reactions where two molecules are joined together are known as:
a) Hydrolases
b) Ligases
c) Lyases
d) Isomerases
Which of the following is a common cofactor required by many enzymes?
a) Calcium
b) Sodium
c) Magnesium
d) Potassium
Enzymes that cleave bonds by adding water are called:
a) Oxidoreductases
b) Transferases
c) Hydrolases
d) Lyases
The term used to describe the maximum rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is:
a) Km
b) Vmax
c) Turnover number
d) Michaelis constant
The amount of substrate required to reach half of the maximum reaction velocity is known as:
a) Vmax
b) Km
c) Turnover number
d) Enzyme efficiency
Enzymes that catalyze the rearrangement of molecular structures are called:
a) Isomerases
b) Ligases
c) Lyases
d) Transferases
Which enzyme is responsible for the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen?
a) Catalase
b) Amylase
c) Lipase
d) Protease
Enzymes that catalyze the removal of a group of atoms from a substrate are known as:
a) Hydrolases
b) Lyases
c) Ligases
d) Transferases
Enzymes that require metal ions for their activity are called:
a) Apoenzymes
b) Holoenzymes
c) Cofactors
d) Coenzymes
The concept that enzyme activity can be regulated by molecules that bind to sites other than the active site is known as:
a) Allosteric regulation
b) Competitive inhibition
c) Non-competitive inhibition
d) Substrate-level regulation
Enzymes that catalyze reactions by adding or removing a carbon dioxide molecule are called:
a) Lyases
b) Hydrolases
c) Ligases
d) Transferases
Which type of inhibition involves the binding of an inhibitor to the active site of an enzyme?
a) Competitive inhibition
b) Non-competitive inhibition
c) Uncompetitive inhibition
d) Allosteric inhibition
What type of enzyme activity is characterized by the enzyme functioning best at a specific pH level?
a) Temperature dependence
b) pH dependence
c) Substrate concentration dependence
d) Enzyme concentration dependence
Enzymes that facilitate the formation of peptide bonds are known as:
a) Proteases
b) Peptidases
c) Ligases
d) Polymerases
The decrease in enzyme activity due to high temperatures is called:
a) Denaturation
b) Inhibition
c) Activation
d) Stabilization
What is the term used to describe the overall process where an enzyme binds to its substrate and converts it into product?
a) Enzyme activation
b) Enzyme inhibition
c) Enzyme catalysis
d) Enzyme degradation
Enzymes that add or remove hydrogen atoms during a reaction are known as:
a) Oxidoreductases
b) Transferases
c) Hydrolases
d) Lyases
The presence of a coenzyme in an enzyme’s active site is crucial for:
a) Increasing the reaction rate
b) Stabilizing the enzyme structure
c) Providing additional chemical reactivity
d) Binding the substrate
What type of enzyme activity is reduced by the presence of a competitive inhibitor?
a) Vmax
b) Km
c) Turnover number
d) Catalytic efficiency
The enzyme that helps in the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template is called:
a) DNA polymerase
b) RNA polymerase
c) Ligase
d) Helicase
Enzymes that are inactive until a specific molecule binds to them are called:
a) Proenzymes
b) Holoenzymes
c) Apoenzymes
d) Cofactors
The mechanism where an enzyme changes its conformation to facilitate substrate binding is:
a) Lock and key model
b) Induced fit model
c) Competitive model
d) Allosteric model
Enzymes that facilitate the formation of a new bond between two molecules using energy from ATP are known as:
a) Ligases
b) Hydrolases
c) Transferases
d) Isomerases
Which of the following statements about enzymes is incorrect?
a) Enzymes are highly specific for their substrates
b) Enzymes are consumed in the reactions they catalyze
c) Enzymes lower the activation energy of reactions
d) Enzymes can be regulated by various factors
The overall process of enzyme catalysis includes:
a) Substrate binding
b) Formation of the enzyme-substrate complex
c) Conversion of substrate to product
d) All of the above
If you are interested to enhance your knowledge regarding Physics, Chemistry, Computer, and Biology please click on the link of each category, you will be redirected to dedicated website for each category.