Integration of Princely States MCQs with Answers
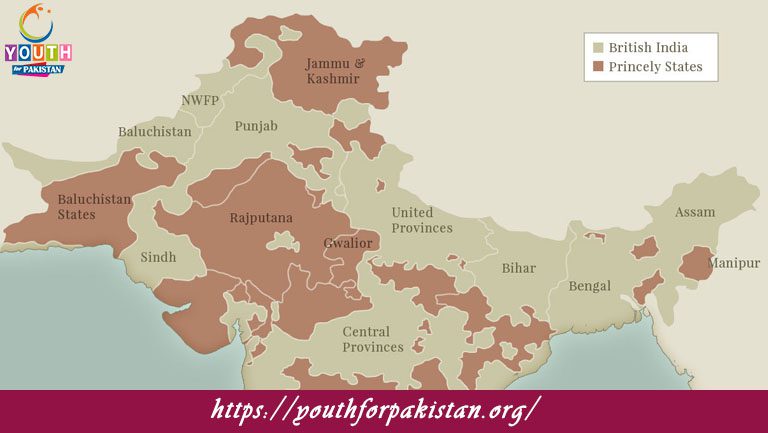
The integration of princely states into Pakistan post-independence was a significant political process. This MCQ set covers the challenges and strategies used to unify the diverse states. Learn about the political challenges of integrating princely states into Pakistan.
What was the primary strategy used by the Indian government to integrate princely states after independence?
a) Diplomatic negotiations
b) Military conquest
c) Economic incentives
d) Cultural assimilation
Which princely state was the first to join the Indian Union after independence?
a) Travancore
b) Jammu and Kashmir
c) Hyderabad
d) Mysore
The merger of which princely state was highly controversial and led to a military intervention by the Indian government in 1948?
a) Junagadh
b) Jodhpur
c) Bhopal
d) Patiala
Which Indian leader played a significant role in negotiating the integration of princely states with India?
a) Jawaharlal Nehru
b) Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel
c) Subhas Chandra Bose
d) Mahatma Gandhi
What was the primary motive behind the integration of princely states into the Indian Union?
a) Economic development
b) National security
c) Cultural diversity
d) Political dominance
Which princely state initially refused to accede to India, leading to the controversial Operation Polo in 1948?
a) Mysore
b) Hyderabad
c) Travancore
d) Jodhpur
What legal framework was created to facilitate the integration of princely states into the Indian Union?
a) Princely States Act
b) Indian Constitution
c) States Reorganization Act
d) Integration and Accession Bill
Which princely state’s integration was complicated by the existence of multiple small states within its territory?
a) Bhopal
b) Jammu and Kashmir
c) Tripura
d) Manipur
The merger of which princely state was primarily facilitated by the efforts of the Dewan of the state, V. P. Menon?
a) Travancore
b) Mysore
c) Hyderabad
d) Cochin
The Instrument of Accession was a legal document used by the princely states to accede to:
a) Pakistan
b) India
c) United Kingdom
d) China
What was the official policy of the Indian government towards the princely states after independence?
a) Non-intervention
b) Military aggression
c) Economic sanctions
d) Diplomatic isolation
The Accession of Jammu and Kashmir to India led to the outbreak of which conflict in 1947?
a) First Kashmir War
b) Indo-Pakistani War of 1947
c) Kargil War
d) Siachen Conflict
What was the primary challenge in integrating the princely state of Manipur into the Indian Union?
a) Political instability
b) Geographical isolation
c) Tribal unrest
d) External interference
The princely state of Travancore was integrated into the Indian Union through the efforts of:
a) V. P. Menon
b) Jawaharlal Nehru
c) C. Rajagopalachari
d) Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel
What was the significance of the merger of the princely state of Mysore into the Indian Union?
a) Economic development
b) Cultural revival
c) Geopolitical stability
d) Integration of South India
Which princely state had a unique political setup and was not fully integrated into the Indian Union until the 1970s?
a) Sikkim
b) Assam
c) Nagaland
d) Meghalaya
The merger of which princely state was characterized by the intervention of the Indian military to suppress a rebellion in the state?
a) Jodhpur
b) Manipur
c) Bhopal
d) Tripura
What was the primary role of the Ministry of States in the integration of princely states into the Indian Union?
a) Economic development
b) Political negotiations
c) Military operations
d) Cultural assimilation
The princely state of Bhopal was integrated into the Indian Union through a formal agreement with the last Nawab of Bhopal, who was:
a) Siddiq Hasan Khan
b) Hamidullah Khan
c) Ghulam Mohammed Khan
d) Yar Mohammad Khan
The merger of which princely state was marked by the signing of the Instrument of Accession by Maharaja Hari Singh in 1947?
a) Manipur
b) Jammu and Kashmir
c) Bhopal
d) Tripura
What was the main consideration for princely states when deciding whether to accede to India or Pakistan after independence?
a) Cultural ties
b) Economic incentives
c) Geographical proximity
d) Security concerns
The role of the Dewan of the princely states was crucial in negotiating the terms of:
a) Economic development
b) Political accession
c) Military cooperation
d) Cultural exchange
The Indian government’s approach towards the integration of princely states was influenced by the principles of:
a) Non-alignment
b) Socialism
c) Secularism
d) Democracy
The merger of which princely state was facilitated by the formal agreement known as the Merger Agreement of Tripura?
a) Jodhpur
b) Manipur
c) Bhopal
d) Tripura
The integration of the princely states into the Indian Union was a crucial step in:
a) Economic development
b) Political consolidation
c) Cultural revival
d) Military expansion
The role of Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel in the integration of princely states earned him the title of:
a) Iron Man of India
b) Father of the Nation
c) Architect of Modern India
d) Defender of the Realm
What was the primary reason for the delay in integrating the princely state of Sikkim into the Indian Union?
a) Political instability
b) Geographical isolation
c) International intervention
d) Cultural resistance
The Indian Independence Act of 1947 granted the princely states the option to accede to either India or:
a) Pakistan
b) United Kingdom
c) China
d) Nepal
The integration of the princely states was crucial for the establishment of a unified:
a) Economic system
b) Defense strategy
c) Political framework
d) Cultural identity
What was the significance of the integration of the princely states for the territorial integrity of India?
a) Establishment of natural boundaries
b) Consolidation of power
c) Prevention of external threats
d) Preservation of cultural heritage
The efforts of the Ministry of States were crucial in ensuring the successful integration of princely states into the:
a) Indian Union
b) United Nations
c) British Empire
d) Soviet Union
The princely state of Jodhpur was integrated into the Indian Union through the signing of the Instrument of Accession by its ruler,:
a) Umaid Singh
b) Hanwant Singh
c) Bhim Singh
d) Ajit Singh
The integration of the princely states into the Indian Union was a testament to the success of India’s policy of:
a) Non-alignment
b) Socialism
c) Secularism
d) Democracy
The merger of which princely state was facilitated by the creation of a Legislative Assembly in the state?
a) Jodhpur
b) Manipur
c) Bhopal
d) Tripura
The Indian government’s policy towards the princely states was influenced by the principles of:
a) Non-alignment
b) Socialism
c) Secularism
d) Democracy
The integration of the princely states into the Indian Union was essential for the establishment of a unified:
a) Economic system
b) Defense strategy
c) Political framework
d) Cultural identity
The role of the Ministry of States was crucial in ensuring the successful integration of princely states into the:
a) Indian Union
b) United Nations
c) British Empire
d) Soviet Union
The princely state of Jodhpur was integrated into the Indian Union through the signing of the Instrument of Accession by its ruler,:
a) Umaid Singh
b) Hanwant Singh
c) Bhim Singh
d) Ajit Singh
The integration of the princely states into the Indian Union was a testament to the success of India’s policy of:
a) Non-alignment
b) Socialism
c) Secularism
d) Democracy
The merger of which princely state was facilitated by the creation of a Legislative Assembly in the state?
a) Jodhpur
b) Manipur
c) Bhopal
d) Tripura
The Indian government’s policy towards the princely states was influenced by the principles of:
a) Non-alignment
b) Socialism
c) Secularism
d) Democracy
The integration of the princely states into the Indian Union was essential for the establishment of a unified:
a) Economic system
b) Defense strategy
c) Political framework
d) Cultural identity
The role of the Ministry of States was crucial in ensuring the successful integration of princely states into the:
a) Indian Union
b) United Nations
c) British Empire
d) Soviet Union
The princely state of Jodhpur was integrated into the Indian Union through the signing of the Instrument of Accession by its ruler,:
a) Umaid Singh
b) Hanwant Singh
c) Bhim Singh
d) Ajit Singh
The integration of the princely states into the Indian Union was a testament to the success of India’s policy of:
a) Non-alignment
b) Socialism
c) Secularism
d) Democracy
The merger of which princely state was facilitated by the creation of a Legislative Assembly in the state?
a) Jodhpur
b) Manipur
c) Bhopal
d) Tripura
The Indian government’s policy towards the princely states was influenced by the principles of:
a) Non-alignment
b) Socialism
c) Secularism
d) Democracy
The integration of the princely states into the Indian Union was essential for the establishment of a unified:
a) Economic system
b) Defense strategy
c) Political framework
d) Cultural identity
The role of the Ministry of States was crucial in ensuring the successful integration of princely states into the:
a) Indian Union
b) United Nations
c) British Empire
d) Soviet Union
The princely state of Jodhpur was integrated into the Indian Union through the signing of the Instrument of Accession by its ruler,:
a) Umaid Singh
b) Hanwant Singh
c) Bhim Singh
d) Ajit Singh
Which Indian state played a crucial role in the integration of princely states into the Indian Union?
a) Hyderabad
b) Mysore
c) Jammu and Kashmir
d) Travancore
Which Indian political leader played a significant role in the integration of princely states into the Indian Union?
a) Jawaharlal Nehru
b) Sardar Patel
c) Mahatma Gandhi
d) Subhas Chandra Bose
What was the primary method used by the Indian government to integrate princely states into the Indian Union?
a) Diplomacy
b) Military force
c) Economic incentives
d) Cultural assimilation
Which princely state initially refused to accede to India and had to be persuaded through a police action in 1948?
a) Hyderabad
b) Jodhpur
c) Bhopal
d) Udaipur
Which princely state was the first to accede to India after independence in 1947?
a) Travancore
b) Mysore
c) Jammu and Kashmir
d) Manipur
Which act allowed the British Indian provinces to join either India or Pakistan after independence?
a) Government of India Act, 1935
b) Indian Independence Act, 1947
c) Indian Councils Act, 1909
d) Montagu-Chelmsford Reforms
Which princely state was known for its unique stand of remaining independent after India’s independence in 1947?
a) Junagadh
b) Jaisalmer
c) Jhalawar
d) Jaipur
What was the term used to describe the political agreements between the Indian government and the rulers of princely states during the integration process?
a) Annexation treaties
b) Integration pacts
c) Merger agreements
d) Sovereignty compacts
What was the primary reason behind the delayed integration of princely states into the Indian Union after independence?
a) Lack of resources
b) Geographical remoteness
c) Internal conflicts
d) Ruler’s resistance
Which princely state was known for its strategic location and played a crucial role in the Indo-Pakistani wars of 1947 and 1965?
a) Jodhpur
b) Bikaner
c) Jammu and Kashmir
d) Alwar
What was the official instrument used by the Indian government to facilitate the accession of princely states into the Indian Union?
a) Accession document
b) Merger agreement
c) Annexation treaty
d) Integration memorandum
Which Indian leader played a crucial role in convincing the Nizam of Hyderabad to accede to India in 1948?
a) Mahatma Gandhi
b) Jawaharlal Nehru
c) Sardar Patel
d) Rajendra Prasad
The merger of which princely state with India led to the incorporation of the territories of Goa, Daman, and Diu into the Indian Union in 1961?
a) Travancore
b) Mysore
c) Hyderabad
d) Baroda
What was the term used for the Indian government’s military operation to persuade the Nizam of Hyderabad to accede to India in 1948?
a) Operation Unity
b) Operation Vijay
c) Operation Polo
d) Operation Desert Storm
What was the title given to the Indian political leaders who were responsible for negotiating with the rulers of princely states during the integration process?
a) Integration Commissioners
b) Accession Envoys
c) Merger Representatives
d) Political Agents
What was the term used for the territories that were under the indirect rule of the British Crown in India before independence?
a) Crown territories
b) Feudatory states
c) Protectorates
d) Royal enclaves
Which princely state acceded to India in 1949 after a referendum was held to decide its future?
a) Manipur
b) Tripura
c) Sikkim
d) Assam
What was the term used for the decision-making body that facilitated the accession of princely states to either India or Pakistan after independence?
a) Political Advisory Council
b) Ruling Council
c) Accession Committee
d) Chamber of Princes
Which Indian state was known for its delayed integration due to internal political unrest and the strong position taken by its ruler?
a) Manipur
b) Tripura
c) Mysore
d) Jammu and Kashmir
Which princely state acceded to India after an armed rebellion against the ruler’s decision to accede to Pakistan in 1947?
a) Jodhpur
b) Jaisalmer
c) Jhalawar
d) Junagadh
Which princely state was known for its complex political situation that involved both its Hindu and Muslim populations during the integration process?
a) Jodhpur
b) Jaisalmer
c) Jhalawar
d) Junagadh
The process of integrating princely states into the Indian Union was primarily facilitated by the:
a) Indian National Congress
b) British Parliament
c) All India Muslim League
d) Chamber of Princes
Which princely state was known for its strategic location and its role in the territorial disputes between India and Pakistan after independence?
a) Bhopal
b) Manipur
c) Tripura
d) Jammu and Kashmir
What was the term used for the political agreement made between the ruler of a princely state and the Indian government to ensure the state’s integration into the Indian Union?
a) Instrument of Accession
b) Merger Declaration
c) Sovereignty Agreement
d) Unity Pact
The princely state of Travancore acceded to India in 1949 after the merger with which other princely state?
a) Kochi
b) Cochin
c) Madras
d) Malabar
What was the term used for the political decision made by the Indian government to incorporate certain princely states into the Indian Union?
a) Annexation
b) Merger
c) Acquisition
d) Subjugation
The ruler of which princely state played a crucial role in the establishment of the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir after independence?
a) Jodhpur
b) Jaisalmer
c) Jhalawar
d) Junagadh
The princely state of Bhopal acceded to India in 1949 after the ruling Begum signed an agreement with which Indian political leader?
a) Jawaharlal Nehru
b) Sardar Patel
c) Mahatma Gandhi
d) Subhas Chandra Bose
What was the term used for the Indian government’s policy to ensure the integration of princely states into the Indian Union after independence?
a) Princely Reconciliation
b) Integration Resolve
c) Accession Diplomacy
d) Merger Policy
The princely state of Baroda acceded to India in 1949 under the rule of which ruler?
a) Sayajirao Gaekwad III
b) Pratap Singh Rao Gaekwad
c) Maharaja Fatehsingh Rao Gaekwad
d) Pratapsinhrao Gaekwad



