Subatomic Particles MCQs with Answers
Welcome to the Subatomic Particles MCQs with Answers, it helps learners quickly identify areas for improvement in Subatomic Particles Online Test.
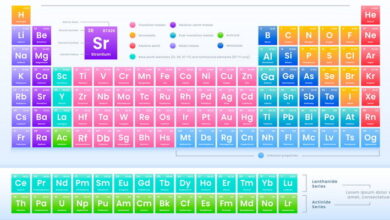
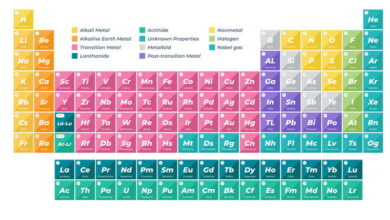
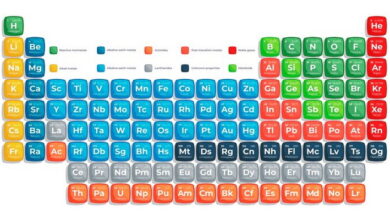
| Subatomic particles are the fundamental constituents of atoms, consisting of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons carry a positive charge and determine the atomic number of an element, while neutrons have no charge but contribute to the mass of the atom. Electrons are negatively charged and orbit the nucleus, determining the atom’s size and reactivity.
To effectively learn about subatomic particles, engaging with MCQs on subatomic particles is crucial. These questions cover a range of topics, from identifying the properties and characteristics of protons, neutrons, and electrons to understanding their roles in atomic structure and chemical behavior. Subatomic particles quiz questions typically test knowledge on atomic mass, isotopes, electron configuration, and the principles of atomic bonding. |
Subatomic Particles Online Quiz
By presenting 3 options to choose from, Subatomic Particles Quiz which cover a wide range of topics and levels of difficulty, making them adaptable to various learning objectives and preferences. You will have to read all the given answers of Subatomic Particles Questions and Answers and click over the correct answer.
- Test Name: Subatomic Particles MCQ Quiz Practice
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 40
- Total Marks: 40
- Time: 40 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test. Practice each quiz test at least 3 times if you want to secure High Marks. Once you are finished, click the View Results button. If any answer looks wrong to you in Quiz, simply click on question and comment below that question, so that we can update the answer in the quiz section.
Download Certificate of Subatomic Particles Test
On the end of Quiz, you can download the certificate of the quiz if you got more than 70% marks.
Subatomic Particles Flashcards
The subatomic particle with a positive charge found in the nucleus of an atom is called a __________.
proton
The subatomic particle with a negative charge that orbits the nucleus of an atom is called a __________.
electron
Isotopes of an element have the same number of __________ but different numbers of neutrons.
protons
The particle associated with the Higgs field, giving particles their mass, is the __________.
Higgs boson
The subatomic particle with no charge and a mass of approximately 1 atomic mass unit (amu) is the __________.
neutron
The concept of electrons existing in fixed orbits around the nucleus of an atom was proposed by __________.
Niels Bohr
The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of __________ in an atom of that element.
protons
Isotopes of an element have the same number of __________ but different numbers of neutrons.
protons
The region around the nucleus of an atom where electrons are likely to be found is called the __________.
electron cloud
If you are interested to enhance your knowledge regarding Physics, Computer, and Biology please click on the link of each category, you will be redirected to dedicated website for each category.