Welcome to the Rate Laws MCQs with Answers, it helps learners quickly identify areas for improvement in Rate Laws Online Test.
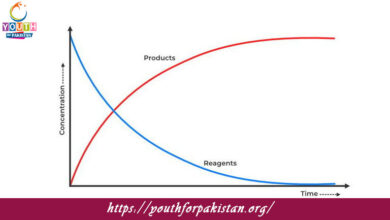
| Rate laws are mathematical expressions that describe the relationship between the rate of a chemical reaction and the concentration of its reactants. They are fundamental in understanding reaction kinetics, as they help predict how changes in concentration affect reaction speed.
For students and professionals aiming to master this topic, Rate Laws MCQs with Answers provide an excellent way to practice and reinforce their understanding. These multiple choice questions cover various aspects of rate laws, including determining reaction orders, calculating rate constants, and interpreting experimental data.
Rate Laws Quiz Questions are designed to test one’s ability to apply theoretical knowledge to practical problems. These quizzes often include scenarios where one must derive the rate law from given data or predict how changes in concentration will affect the reaction rate.
A Rate Laws Practice Test offers a comprehensive review of the subject, allowing individuals to assess their proficiency and identify areas that need further study. Finally, Rate Laws Exam Questions delve deeper into complex concepts, ensuring a thorough understanding of reaction kinetics and the application of rate laws in different contexts. |
Rate Laws Online Quiz
By presenting 3 options to choose from, Rate Laws Quiz which cover a wide range of topics and levels of difficulty, making them adaptable to various learning objectives and preferences. You will have to read all the given answers of Rate Laws Questions and Answers and click over the correct answer.
- Test Name: Rate Laws MCQ Quiz Practice
- Type: Quiz Test
- Total Questions: 40
- Total Marks: 40
- Time: 40 minutes
Note: Answer of the questions will change randomly each time you start the test. Practice each quiz test at least 3 times if you want to secure High Marks. Once you are finished, click the View Results button. If any answer looks wrong to you in Quiz, simply click on question and comment below that question, so that we can update the answer in the quiz section.
Download Certificate of Rate Laws Test
On the end of Quiz, you can download the certificate of the quiz if you got more than 70% marks.
Rate Laws Flashcards

What is the general form of the rate law for the reaction A + B → C?

What is the unit of the rate constant for a first-order reaction?

What is the rate law for a zero-order reaction with respect to A?

For the reaction 2A + B → C, if the rate law is Rate = k[A][B], what is the order with respect to A?

In the rate law Rate = k[A]²[B], what is the overall order of the reaction?

If the rate of a reaction doubles when the concentration of A is doubled, what is the order with respect to A?

For the reaction A + B → products, if Rate = k[A]², what happens to the rate if [A] is tripled?
Increases by a factor of 9

What is the rate law for a reaction that is first order in A and second order in B?

What is the order of a reaction if the rate law is Rate = k?

For the reaction A → products, if the half-life is constant, what is the order of the reaction?

In a first-order reaction, how is the rate related to the concentration of the reactant?

For the reaction 2A → products, if the rate law is Rate = k[A]², what is the order of the reaction?

What is the rate constant for a reaction that is second order overall?

In the rate law Rate = k[A][B], what happens to the rate if [B] is halved?

For the reaction A + B → products, if Rate = k[A][B] and [A] is doubled, what happens to the rate?

What is the rate law for a reaction that is zero order in A and first order in B?

In the rate law Rate = k[A]², what happens to the rate if [A] is reduced by half?
Decreases by a factor of 4

For a reaction with Rate = k[A]²[B], what is the order with respect to B?

What is the unit of the rate constant for a zero-order reaction?

In the rate law Rate = k[A][B], what is the overall order of the reaction?

For a second-order reaction, what is the relationship between half-life and initial concentration?

What is the rate law for a reaction that is second order in A and zero order in B?

If the rate of a reaction does not change with an increase in concentration of the reactants, what is the order of the reaction?

In a reaction with Rate = k[A][B], what happens to the rate if both [A] and [B] are doubled?

For the reaction A + B → C, if Rate = k[A]²[B]³, what is the overall order of the reaction?

What is the rate law for a reaction that is first order in A and zero order in B?

For the reaction 2A + B → products, if Rate = k[A]²[B], what is the order with respect to B?

In the rate law Rate = k[A]³, what happens to the rate if [A] is doubled?
Increases by a factor of 8

For a reaction with Rate = k[A][B], what is the unit of the rate constant?

What is the rate law for a reaction that is zero order in A and second order in B?

In the rate law Rate = k[A][B]², what is the order with respect to A?

For the reaction A + 2B → products, if Rate = k[A][B]², what is the overall order of the reaction?

What is the rate law for a reaction that is second order in A and first order in B?

In the rate law Rate = k[A], what happens to the rate if [A] is tripled?

For a reaction with Rate = k[A], what is the order of the reaction?

What is the unit of the rate constant for a third-order reaction?

In the rate law Rate = k[A][B], what happens to the rate if [A] is halved and [B] is doubled?

For the reaction A + B → products, if Rate = k[A]²[B], what is the order with respect to A?

What is the rate law for a reaction that is first order in A and second order in B?

In the rate law Rate = k[A][B], what happens to the rate if [A] and [B] are both tripled?
Increases by a factor of 9
If you are interested to enhance your knowledge regarding Physics, Computer, and Biology please click on the link of each category, you will be redirected to dedicated website for each category.